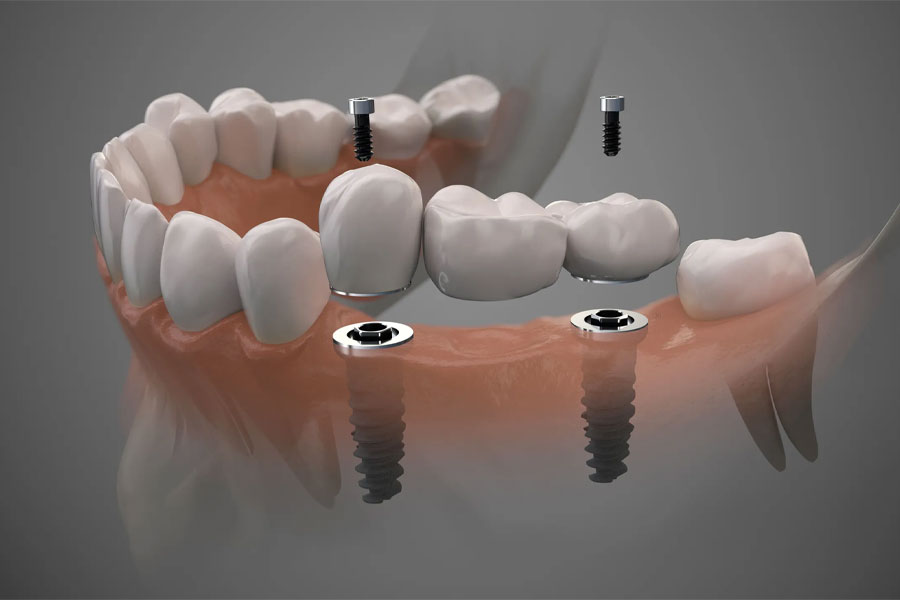
Guided Surgery
Planning: Guided surgery begins with detailed pre-operative planning. Using medical imaging techniques like CT scans, a 3D digital model of the patient's anatomy is created. This model helps surgeons visualize the surgical site in great detail.
Computer Assistance: Specialized software is used to analyze the 3D model and plan the surgery. Surgeons can virtually manipulate and simulate the procedure, making precise decisions about the placement of implants, instruments, or other surgical interventions.
Surgical Guide: A surgical guide is created based on the digital plan. This guide is a custom-made device, often 3D printed, that fits over the patient's anatomy during surgery. It serves as a precise template, ensuring that the surgeon follows the planned path accurately.
Precision Surgery: During the actual surgery, the surgical guide helps guide the surgeon's instruments or implants, ensuring they are placed with high precision according to the pre-operative plan. This minimizes the risk of errors and complications.
Benefits: Guided surgery offers several advantages, including increased accuracy, reduced surgical time, smaller incisions, and decreased patient discomfort. It is commonly used in various medical and dental procedures, such as implant placements, orthopedic surgeries, and craniofacial reconstructions.



